Genetics & Genomics Lesson Plans (10 results)
What traits are heritable? How different is your DNA from a frog's, a mouse's or even your relative's? Can your genes tell doctors what is the right dose of a medicine for your body? These are the types of questions scientists are answering with genetics and genomics. By studying individual genes as well as genomes, the whole set of DNA belonging to an organism, scientists hope to get a more complete understanding of how our bodies work and develop better disease treatments.
|
Select a resource
Sort by
|
Lesson Plan
Grade: 6th-8th
24 reviews
In this lesson, students will model how traits are passed on from parents to their offspring by creating baby aliens based on their parents' traits. As students compare the physical features of their alien families, they will be able to make the connection between an organism's genotype and phenotype. Students will also learn the difference between dominant and recessive traits.
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Featured
Lesson Plan
Grade: 6th-8th
7 reviews
Junkbots are easy-to-build robots that you can make using a simple circuit and some recyclable materials. In this lesson, your students will learn about engineering design as they compete to build the fastest robot. No previous robotics experience is required!
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Lesson Plan
Grade: 6th-8th
5 reviews
Explore genetic variation through the world of taste in this problem-solving lesson plan. Working both individually and collaboratively, students figure out what kind of tasters they are, what this means about their own genetics, and how genetic mutations can lead to functional differences. This activity provides a hands-on, personalized opportunity to learn about how genotypes and phenotypes align.
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
New
Lesson Plan
Grade: 6th-12th
Create a two-part system for filtering greywater. Teams will focus on communication and systems engineering as they build separate components to filter solid and liquid waste and then combine them into one device.
Learning Objectives
Students will:
Consider the potential effects of drought and how greywater could be part of the solution.
Design a system for filtering out solid waste or liquid waste.
Consider effective communication strategies with their team.
Collaborate on their design…
Read more
Lesson Plan
Grade: 6th-12th
5 reviews
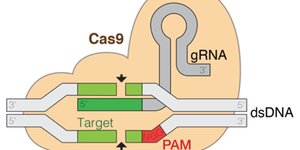
In this lesson plan, students will take a closer look at the most recent developments in gene editing. Specifically, they will learn about the CRISPR technology using various interactive simulations and other resources. Based on their gained knowledge, students will create a model of the CRISPR-Cas9 components and create a stop-motion animation video of the molecular mechanism of CRISPR-Cas9.
Remote learning adaptation:
This lesson plan can be conducted remotely. Students can work…
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Lesson Plan
Grade: 6th-8th
5 reviews
Using the context of apples, students will apply their knowledge of heredity and genetics to distinguish between sexual and asexual reproduction as they explain how new varieties of apples are developed and then propagated to meet consumer demand for a tasty, uniform, consistent product.
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Lesson Plan
Grade: 9th-12th
2 reviews
This lesson introduces students to the relationships between chromosomes, genes, and DNA molecules. Using the example of a strawberry, it also provides activities that clearly show how changes in the DNA of an organism, either naturally or artificially, can cause changes.
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Lesson Plan
Grade: 3rd-5th
2 reviews
Students will explore heredity concepts by comparing observable traits of apples and onions, collecting data on the traits of different apple varieties, and learning about apple production. Additional activities include hands-on methods for testing apple ripeness.
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Lesson Plan
Grade: 6th-12th
4 reviews
We hear about COVID-19 variants all the time, but what is a virus variant, how do they come about, and why do they matter? Students will explore these question and more in this lesson plan. They will use SimPandemic, a free online tool, to model what COVID-19 outbreaks look like when communities are exposed to different COVID-19 variants and understand how genetic mutations in a virus can lead to functional changes.
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Lesson Plan
Grade: 9th-12th
Students will compare and contrast methods of selective plant breeding, describe the scientific process of creating a genetically modified plant, compare genetically modified soybean seeds to conventional soybean seeds, describe the impact weeds have on plant growth, and understand how a genetically modified seed can help farmers manage weeds.
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Lesson Plan
Grade: 6th-8th
1 review
This lesson uses problem-solving and logical thinking to introduce students to phylogenetic trees. Students will create, organize, and structure data to explore patterns of heredity.
Learning Objectives
Students will:
Explore how phylogenetic trees organize species based on shared characteristics.
Discover both the power and the limitations of phylogenetic trees as a tool for making inferences about the evolutionary history of different species.
Engage in authentic science practices…
Read more
Lesson Plan
Grade: 9th-12th
3 reviews
This lesson compares and contrasts prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and examines the form and function of the plasmid found in prokaryotic cells. Students will then use these principles to simulate how a desirable gene can be isolated and inserted into a plasmid as one step in the process of creating a genetically modified organism (GMO).
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
|
Explore Our Science Videos
Make an LED Lightsaber with a Straw
Balloon car lesson plan
Sweet Earthquake Shake- STEM activity